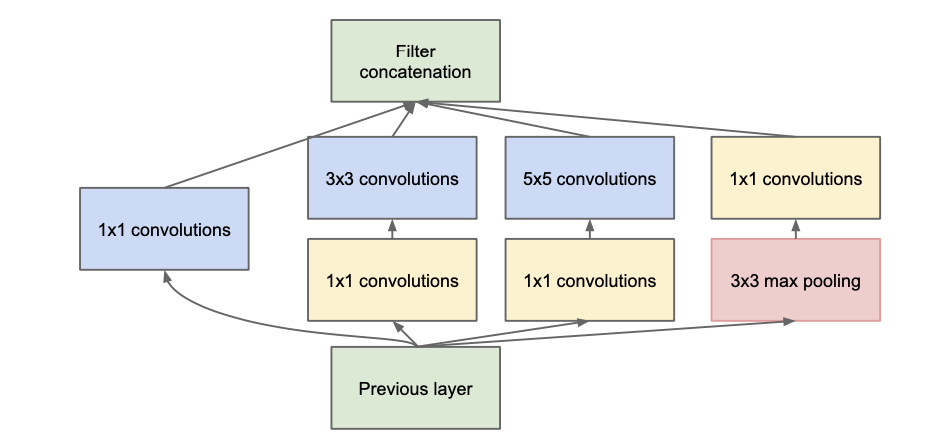
GoogLeNet[1] is used to classify images with inception v1. There are some details of reading and implementing it.
Contents
Paper & Code & note
Paper: Going deeper with convolutions(CVPR 2015 paper)
Code: PyTorch
Note: GoogLeNet
Paper
Abstract
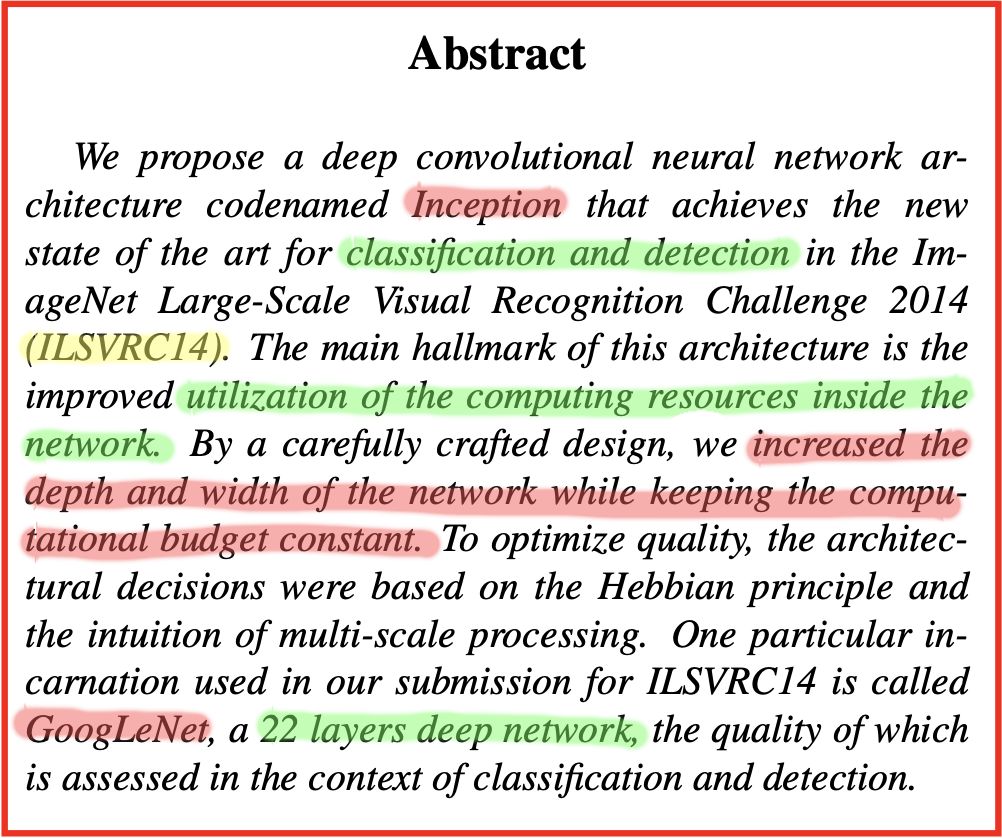
As abstract of the paper, their work mainly proposed a CNN architecture codenamed Inception, so that to build a inception-based network with 22 layers called GoogLeNet for classification and detection.
- bulid Inception architecture based on the
Hebbian principleand the intuition ofmulti-scaleprocessing.- It increased the depth and width of the network while keeping the computational budget constant.
Problem Description

It shows the purpose of GoogLenet and the drawbacks of exsiting methods about solving this problem.
Problem Solution

It proposal a network architecture named Inception, including
what it can doandhow it works.
Conceptual Understanding
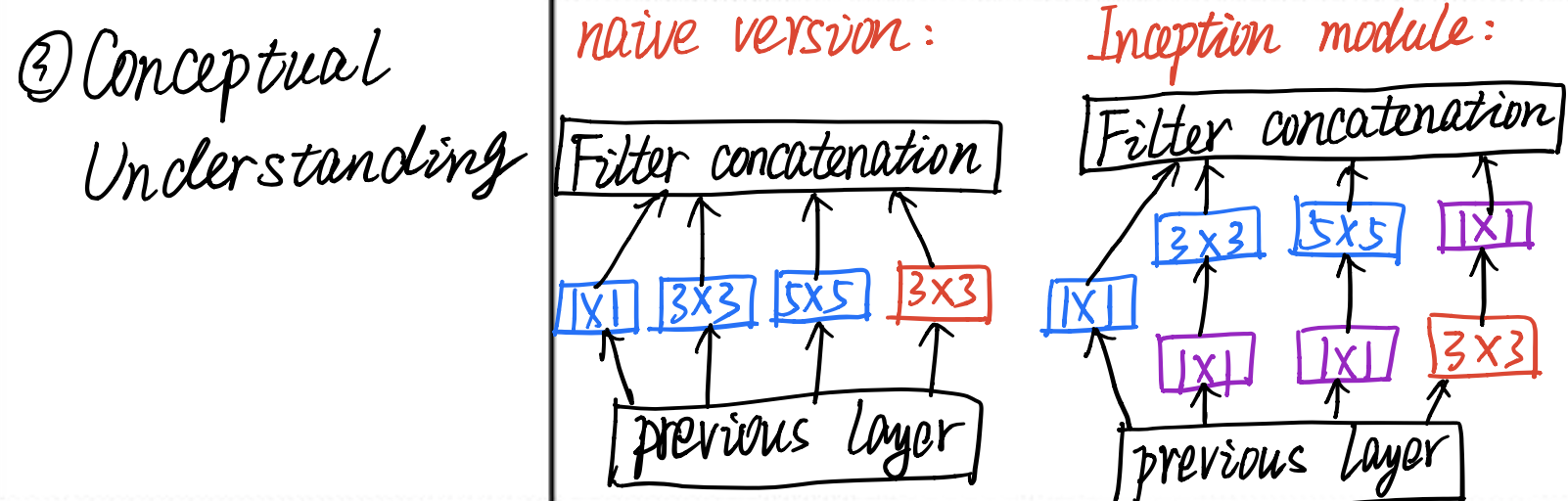
It describes two version of architecture of Inception, including
naive versionandinception_v1.
Core Conception
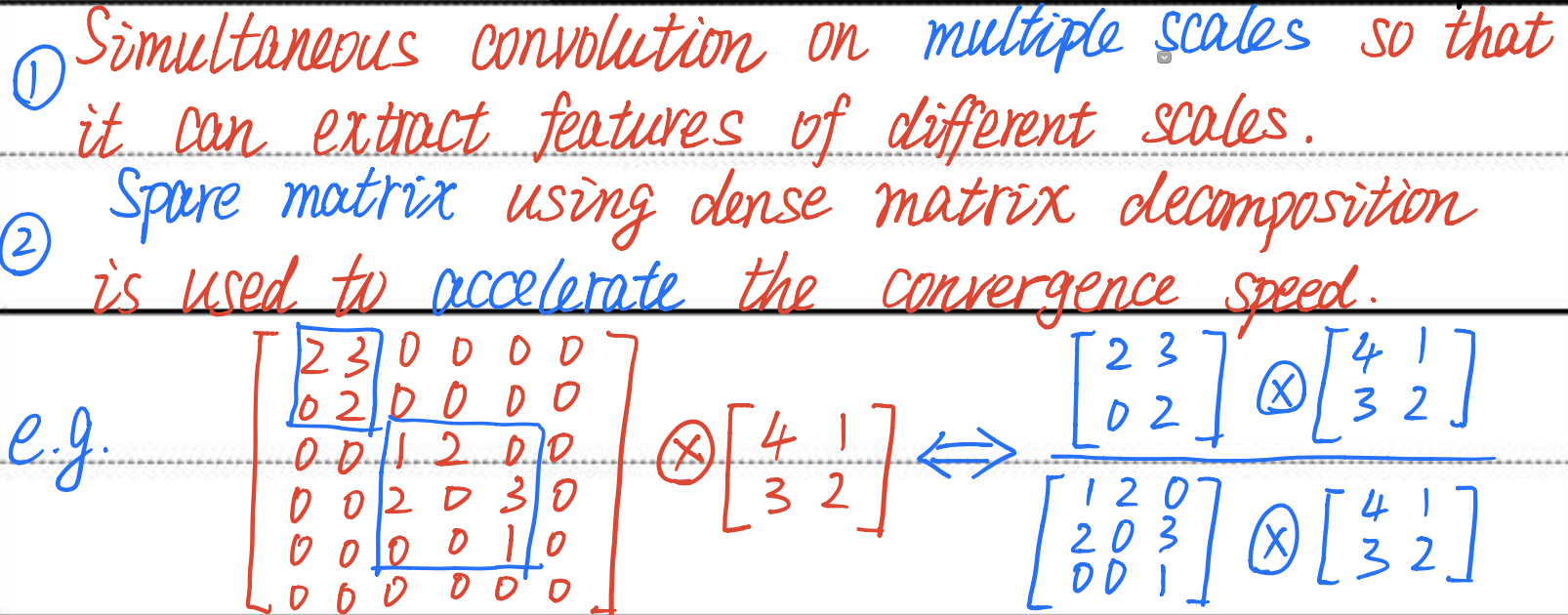
It denotes the
most importantconception of Inception mudules, and it explains convolution on multiple scales to extract features, and using spare matrix to accelerate convergence speed with ainstance.
Besides, the network architecture shows below.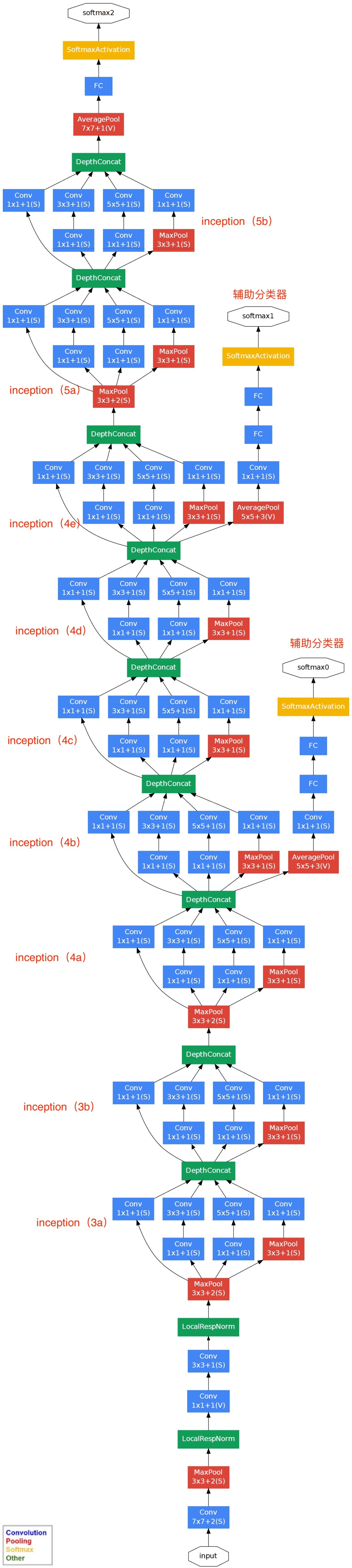
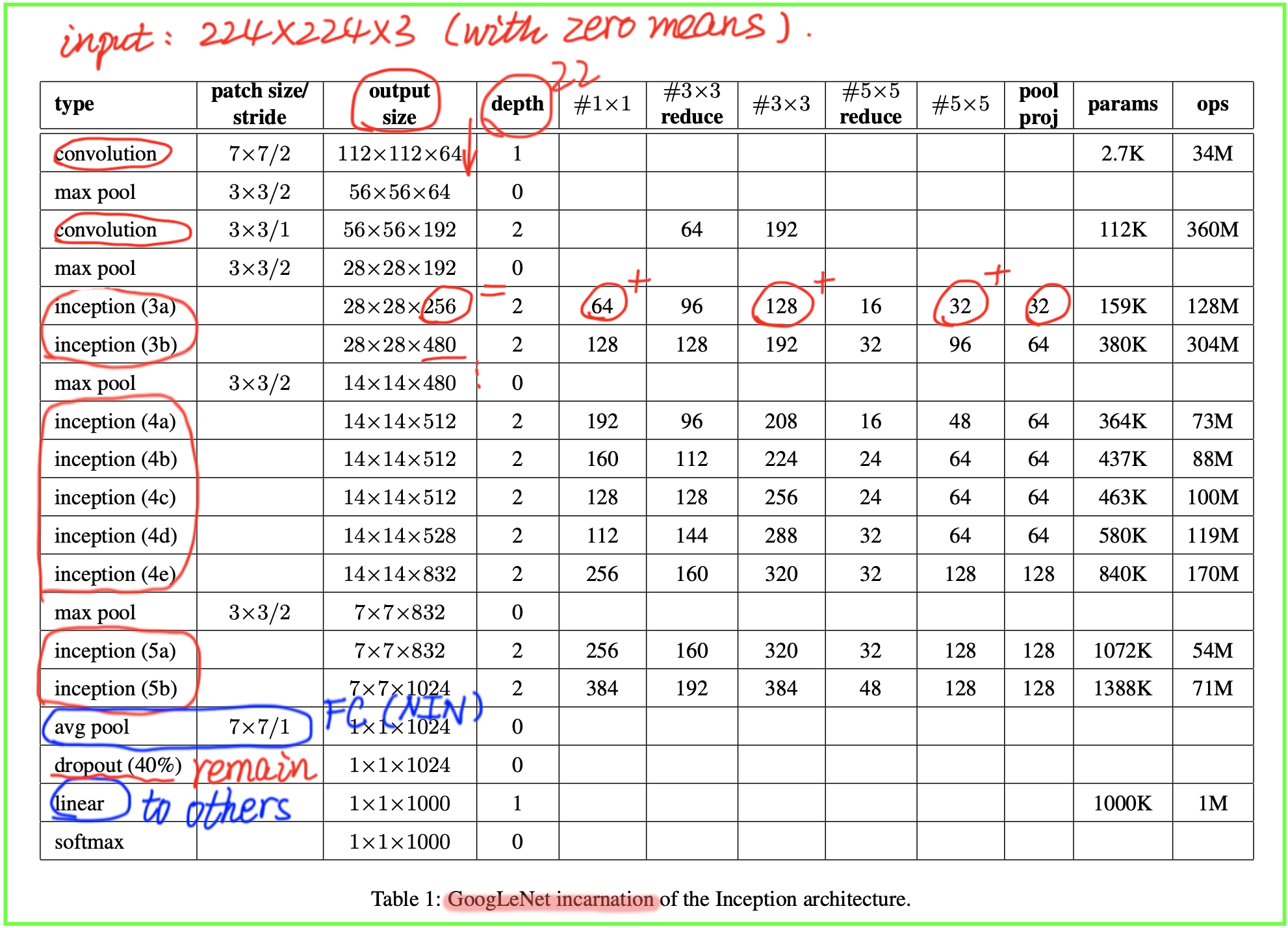
Code
The complete code can be found in here.
Details of implementation
the whole network architecture: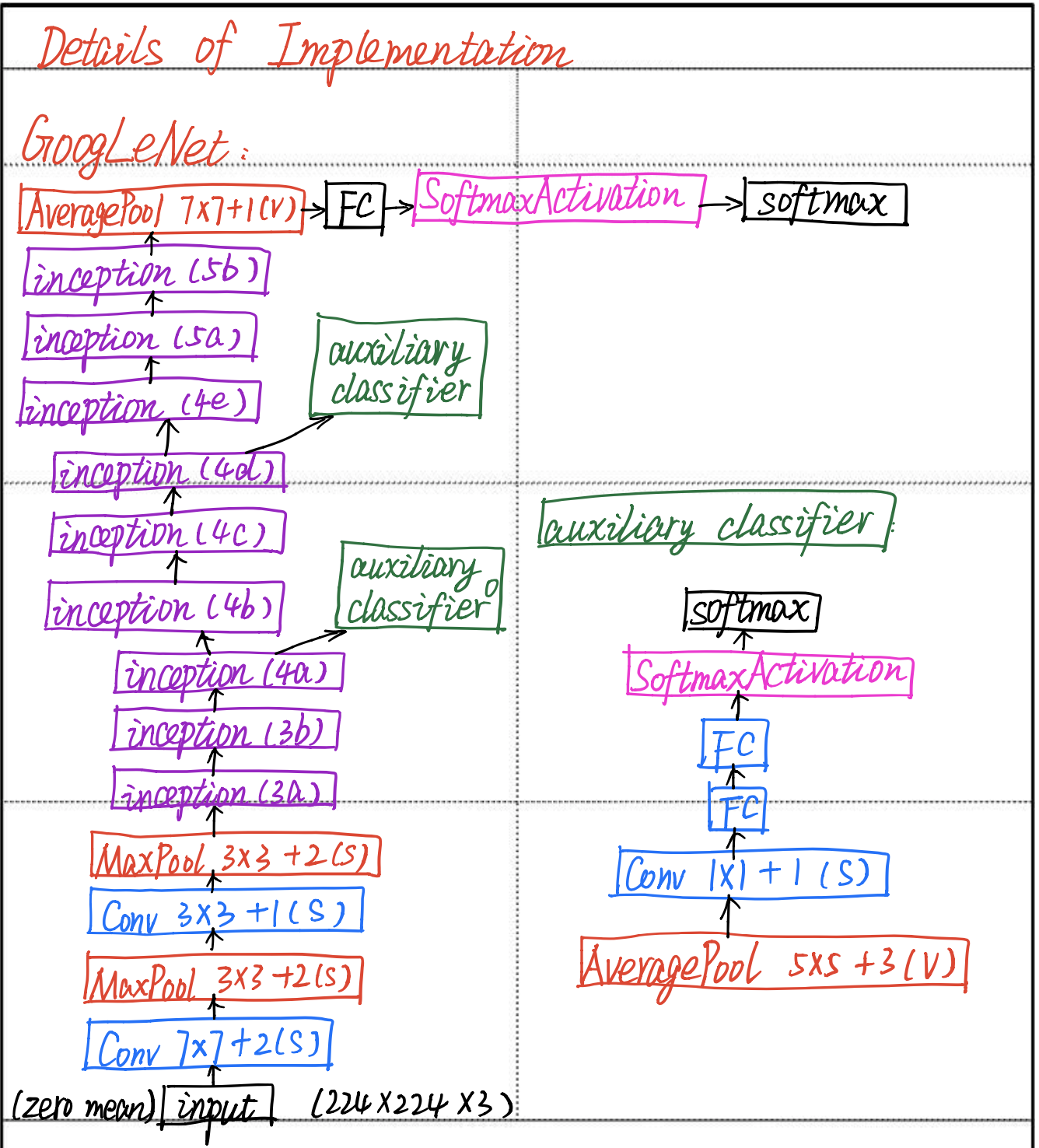
the details of googlenet: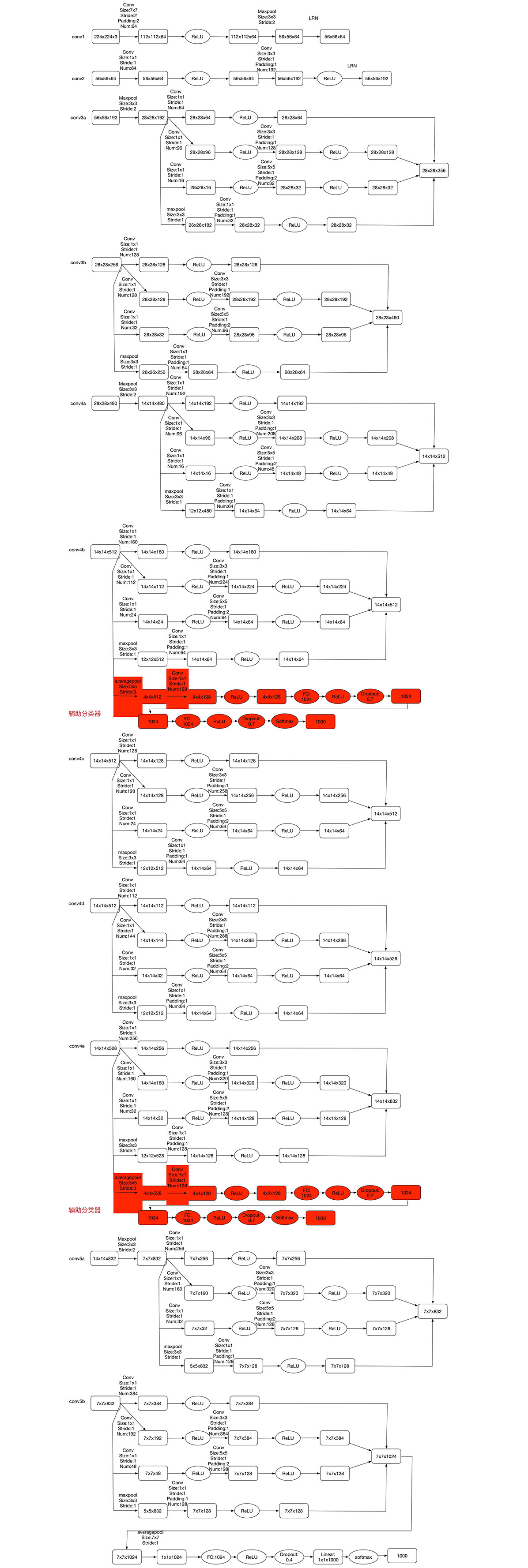
the step of implementation:
It includes the whole network architeture and the implementation of auxiliary classfier.
Inception
class BasicConv2d(nn.Module): |
class Inception(nn.Module): |
Auxiliary classifer
class InceptionAux(nn.Module): |
GoogLeNet
class GoogLeNet(nn.Module): |
Note
More details of Inception about implementation can be found in [2].
More details of conception about multi-scale and spare matrix can be found in [3].
References
[1] Szegedy, Christian, et al. “Going deeper with convolutions.” Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2015.
[2] Bing Xue. “Big word about CNN classic model.” https://my.oschina.net/u/876354/blog/1637819.
[3] Lei Zhang. “Deep understanding GoogLeNet architecture.” https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/32702031.